To share content in a distributed collaboration with other organizations, an administrator begins by creating the collaboration and collaboration workspace, linking a group to the workspace, and inviting participants to the collaboration. The organization that creates the collaboration is the host, and other participating organizations are guests. These concepts are described in more detail in the following sections.
Note:
To learn how to set up a collaboration, see Create a collaboration.
Collaboration host and guests
A collaboration consists of one host and one or more guests. Collaboration is initiated when an administrator of the host organization sends an invitation to an administrator of one or more participating guest organizations. The administrator of each guest organization then accepts the invitation and sends their acknowledgement to the host's administrator, who accepts the acknowledgement to complete the trusted connection.
Host
A host is defined as the organization where the collaboration is initiated. In a collaboration in which an ArcGIS Online organization is participating, the host is always the ArcGIS Online organization.
The administrator in the host organization must do the following to create a collaboration and share content among guest organizations:
- Create a collaboration and collaboration workspace
- Link a group to the workspace
- Invite guests to the collaboration
- Define the access mode for each guest
Guests
Guests in a collaboration are defined as ArcGIS Enterprise 10.5.1 and later deployments that are invited by the host. An administrator of each guest organization does the following to join a collaboration and share content among participants:
- Accept an invitation to collaborate
- Link a group to the workspace
- Configure sync settings for the collaboration workspace
Collaborations and workspaces
A workspace is a conceptual space in a collaboration that represents a project, an initiative, or another organizing principle. Every collaboration must have at least one workspace, but a collaboration can have more than one if needed to support a specific collaboration scenario. Multiple workspaces can be used to organize larger collaborations that span multiple projects and initiatives for the same set of participants.
The collaboration workspace is a logical construct rather than a physical data container; it does not hold any content. Rather, to share data in a collaboration, members share content with a group that has been linked to the workspace. For more information, see Workspaces and groups.
When configuring a collaboration workspace, host administrators specify how feature layers will be shared (by reference or as copies) and define the access mode for each collaboration guest. Guest administrators configuring a workspace specify how feature layers will be shared, and define how data will be synchronized. The host and guests only see the workspace name and description; details about the individual groups that are linked to the workspace are not exposed to collaboration participants.
The concept of a collaboration workspace and its relationship to participants, groups, and workspace access modes is depicted below.
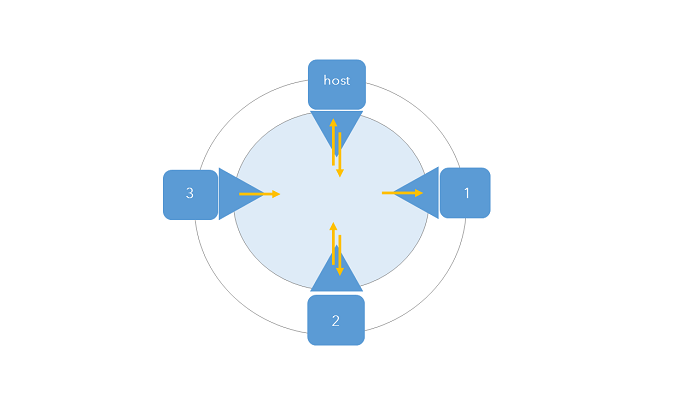
Here are the key points to understanding the diagram:
- The outer circle represents an entire collaboration and its set of trusted participants.
- The inner, shaded circle represents the collaboration workspace.
- Each square represents a collaboration participant; the host is marked as such, and each guest is numbered accordingly.
- Each triangle represents a group that belongs to a collaboration participant and is linked to the collaboration workspace.
- The collaboration host has defined workspace access for itself and participant 2 as Send and Receive.
- The collaboration host has defined workspace access for participant 1 as Receive.
- The collaboration host has defined workspace access for participant 3 as Send.
Collaboration using multiple workspaces
Consider the first scenario in About Distributed Collaboration in which the planning department and community development department are participating in an existing collaboration. Recently, both departments have extended their scope to work on three projects together, one for each new mixed-use development. The teams want to keep data and contents organized by development project, so they have leveraged three workspaces, one for each project.
As the host, the community development department also wants to use workspaces to define the planning department's access mode: they should only be able to send data for the two new projects, but they will be able to send and receive for the existing project. They can also choose to now share feature layers as copies for certain projects, while project data for the other mixed-use development is shared by reference.
To learn how the collaboration host can create additional workspaces, see Manage collaborations.
Workspaces and groups
In a collaboration, content is shared through collaboration groups. Each participant in the collaboration links a group from their organization to the workspace. All shared content appears directly in the group that each participant linked to the workspace. Each participant can link a single group to a workspace. Therefore, if a participant has three groups containing collaboration content—for example, groups for Project A, Project B, and Project C—three workspaces must be created.
The content in the groups is shared according to a schedule set by the guests for each collaboration workspace. Leaving or deleting a workspace will not delete the group. For more information on leaving or deleting a workspace, see Manage collaborations.
Tip:
Groups linked to collaboration workspaces are marked with a collaboration badge on the Overview tab of the group page.
Access modes for workspaces
Content is shared in a collaboration when users share their content with a group that has been linked to a collaboration workspace. The collaboration host is responsible for defining the access mode each guest has to each workspace. The access mode controls how content is shared in the workspace. Access mode options are send only, receive only, and send and receive. Access modes are defined separately for each guest in the collaboration—for example, one guest might have receive access in a workspace while another has send access. In a collaboration that uses multiple workspaces, each guest can have the same access mode or different access modes across the different workspaces as needed.
Note:
Collaboration hosts can always send and receive content.
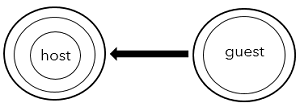
Send only
When the host selects Send as the access mode for the guest, the guest can send content to the host but does not receive any content from the host.
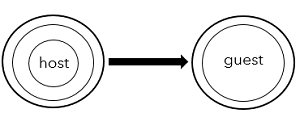
Receive only
When the host selects Receive as the access mode for the guest, the guest will receive content from the host but cannot send any content to the host.
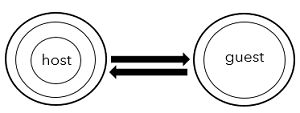
Send and Receive
When the host selects Send and Receive as the access mode for the guest, the guest can send content to, and receive content from, the host. The Send and Receive access mode cannot be used to handle back-and-forth editing of a single dataset between host and guest.
Defining workspaces and access modes
The collaboration host must establish how content is updated for each participating group. Each collaboration guest can set up their groups to synchronize item changes live or at scheduled intervals. For more information, review details to configure sync settings.
The host can create additional workspaces by following the steps in Manage collaborations as a host. Once created by the host, the new workspaces will become available to guests as part of the next scheduled collaboration synchronization. Once available to the guest, the guest organization's administrator can join these new workspaces just as they did with the original workspace. For details, see Manage collaborations as a guest.